***
title: Set up a runner to use a proxy server
updated: 2025-11-21T00:00:00.000Z
slug: docs/monitoring-your-api/runners/proxy-server/runners-proxy-server
max-toc-depth: 2
plan: beta
----------
Private API Monitoring is available with [Postman Basic, Professional, and Enterprise plans](https://www.postman.com/pricing/). To enable Private API Monitoring in your Enterprise team, contact your Postman Customer Success Manager.
You can configure a runner to route HTTP and HTTPS traffic generated during monitor runs through a proxy server that enforces outbound request policies. When you [start a runner](/docs/monitoring-your-api/runners/set-up-a-runner-in-your-network/) with the Postman CLI, you can specify an [external proxy server](#external-proxy-server) URL your organization already uses. Instead, you can use Postman's [built-in proxy server](#built-in-proxy-server) with a runner authorization service you've configured to decide which requests from the runner are allowed or blocked. If required by your external proxy server or runner authorization service, you can [add custom CA certificates](#custom-ca-certificates).
Learn more about the [`postman runner start` command](/docs/postman-cli/postman-cli-options/#postman-runner-start) and its supported options.
## External proxy server
You can use your organization’s existing external proxy server to route and inspect outbound traffic generated by monitor runs. This is useful if your organization already operates a proxy for enforcing outbound network policies, such as allowlisting destinations.
To use an external proxy server, start the runner with the Postman CLI and use the `--proxy` option to specify the external proxy server URL.
```bash wordWrap
postman runner start --proxy --id --key
```
Instead of specifying the `--proxy` option, you can define the proxy server URL using the `HTTP_PROXY` and `HTTPS_PROXY` environment variables.
## Built-in proxy server
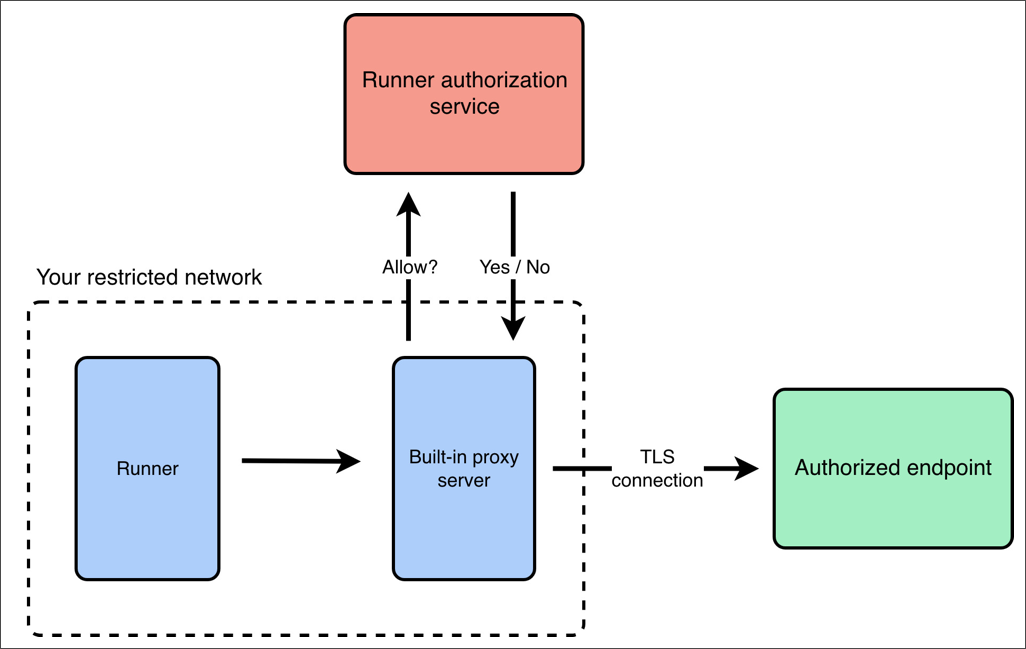
You can use the built-in proxy server to route and inspect outbound traffic generated by monitor runs using rules defined in your runner authorization service. This is useful when you need to enforce outbound access controls, such as restricting allowed domains or methods, without deploying or managing your own proxy server.
To use the built-in proxy server, first set up a runner authorization service with rules that determine which outbound requests are allowed or blocked. Once the authorization service is deployed and running, start the runner with the Postman CLI. Use the `--egress-proxy` option to enable the built-in proxy server, and the `--egress-proxy-authz-url` option to specify the URL of your runner authorization service. For more details, see [Start a runner with the built-in proxy server](/docs/monitoring-your-api/runners/proxy-server/use-built-in-proxy-server/).
```bash wordWrap
postman runner start --egress-proxy --egress-proxy-authz-url --id --key
```
Instead of specifying the `--egress-proxy-authz-url` option, you can define the runner authorization service URL using the `POSTMAN_RUNNER_AUTHZ_URL` environment variable.
When the built-in proxy is enabled, the following happens:
* The runner routes all outbound HTTP and HTTPS traffic through the built-in proxy.
* For each outbound request, the proxy references a runner authorization service that determines if the request is allowed or blocked.
* The proxy only forwards approved requests to their final destination.
* All traffic remains end-to-end encrypted, including HTTPS traffic. The proxy inspects outbound traffic and enforces policies defined by your runner authorization service.
## Custom CA certificates
You can specify custom CA certificates if your external proxy server or runner authorization service require them. Use the `--ssl-extra-ca-certs` option to specify a path to the file in PEM format. Note that the PEM file can have multiple certificates.
```bash wordWrap
postman runner start --ssl-extra-ca-certs --proxy --id --key
```