# The Start block
 The **Start** block is automatically added to every new flow. It triggers connected blocks to run, but connecting blocks to the **Start** block is optional. You can add inputs to this block that receive data from [scenarios](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/). You can also change the **Start** block to a [**Request**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/request/) or [**Schedule**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/schedule/) block so you can [deploy](/docs/postman-flows/reference/flows-actions-overview/) the flow to the Postman cloud.
## Inputs
By default, the **Start** block has no input ports. You can [add inputs](#receive-data-with-inputs) as desired. When you add an input to the **Start** block, Postman Flows creates a **Start Trigger** [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/) and adds the inputs to it as key-value pairs. The input's name is the key, and the value is empty until you edit the scenario.
## Output
By default, the **Start** block has a single output port you can connect to other blocks. Any blocks connected to the **Start** block's output port will run when you click the **Run** button. If you add inputs to the **Start** block, each new input will have its own output port that sends data defined in the flow's [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/).
## Setup
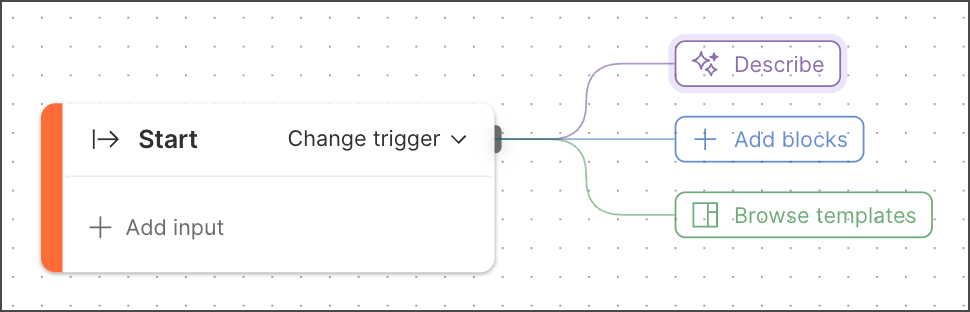
The **Start** block appears automatically on every new flow's canvas. A new **Start** block is connected to three buttons you can click to do the following:
*
The **Start** block is automatically added to every new flow. It triggers connected blocks to run, but connecting blocks to the **Start** block is optional. You can add inputs to this block that receive data from [scenarios](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/). You can also change the **Start** block to a [**Request**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/request/) or [**Schedule**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/schedule/) block so you can [deploy](/docs/postman-flows/reference/flows-actions-overview/) the flow to the Postman cloud.
## Inputs
By default, the **Start** block has no input ports. You can [add inputs](#receive-data-with-inputs) as desired. When you add an input to the **Start** block, Postman Flows creates a **Start Trigger** [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/) and adds the inputs to it as key-value pairs. The input's name is the key, and the value is empty until you edit the scenario.
## Output
By default, the **Start** block has a single output port you can connect to other blocks. Any blocks connected to the **Start** block's output port will run when you click the **Run** button. If you add inputs to the **Start** block, each new input will have its own output port that sends data defined in the flow's [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/).
## Setup
The **Start** block appears automatically on every new flow's canvas. A new **Start** block is connected to three buttons you can click to do the following:
*  **Describe** - Open [agent mode](/docs/agent-mode/overview/), where you can describe in plain language what you want your flow to do.
*
**Describe** - Open [agent mode](/docs/agent-mode/overview/), where you can describe in plain language what you want your flow to do.
*  **Add blocks** - Open the [blocks list](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/create/create-blocks/) to add a block.
*
**Add blocks** - Open the [blocks list](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/create/create-blocks/) to add a block.
*  **Browse templates** - Explore the [Flows Catalog](/docs/postman-flows/get-started/flows-catalog/).
### Receive data with inputs
You can add inputs to the **Start** block. Each input will appear as an inline [data block](/docs/postman-flows/reference/overview-data-blocks/). When you add inputs to the **Start** block, Postman Flows automatically creates a [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/) named **Start Trigger**. Each input you create adds an output port to the **Start** block. Each input also appears as a key-value pair in the **Start Trigger** scenario, where the key is the input's name and the value is empty. Edit the scenario to add values to the key-value pairs. The **Start** block will send these values when you run the flow locally.
To add an input to the **Start** block, do the following:
1. In the **Start** block, click
**Browse templates** - Explore the [Flows Catalog](/docs/postman-flows/get-started/flows-catalog/).
### Receive data with inputs
You can add inputs to the **Start** block. Each input will appear as an inline [data block](/docs/postman-flows/reference/overview-data-blocks/). When you add inputs to the **Start** block, Postman Flows automatically creates a [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/) named **Start Trigger**. Each input you create adds an output port to the **Start** block. Each input also appears as a key-value pair in the **Start Trigger** scenario, where the key is the input's name and the value is empty. Edit the scenario to add values to the key-value pairs. The **Start** block will send these values when you run the flow locally.
To add an input to the **Start** block, do the following:
1. In the **Start** block, click  **Add input**. A **String** block is inserted into the **Start** block.
2. (Optional) Click the dropdown list if you want to select a data block other than **String**. Use
**Add input**. A **String** block is inserted into the **Start** block.
2. (Optional) Click the dropdown list if you want to select a data block other than **String**. Use  **Secret** for sensitive string values like API keys. To learn how secret inputs work, see [Secrets in scenarios](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/#secrets-in-scenarios).
3. Enter a name for the input.
4. Edit the **Start Trigger** scenario to assign data to the input.
### Specify inputs for a Flow block
When a [**Flow** block](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/flow-module/) references a flow whose **Start** block has inputs, those inputs appear as named input ports in the **Flow** block. When other blocks send data to these ports, the **Flow** block will send that data to the corresponding inputs in the referenced flow's **Start** block. The values that the referenced flow produces will then be available through the **Flow** block's outputs. To learn more, see [The Flow block](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/flow-module/).
The scenarios you created to provide data to the inputs in the referenced flow's **Start** block won't be available to the **Flow** block. This means that in the flow containing the **Flow** block, you need to add blocks or scenarios to supply data to the inputs.
## Example
Suppose you make the following flow:
**Secret** for sensitive string values like API keys. To learn how secret inputs work, see [Secrets in scenarios](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/#secrets-in-scenarios).
3. Enter a name for the input.
4. Edit the **Start Trigger** scenario to assign data to the input.
### Specify inputs for a Flow block
When a [**Flow** block](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/flow-module/) references a flow whose **Start** block has inputs, those inputs appear as named input ports in the **Flow** block. When other blocks send data to these ports, the **Flow** block will send that data to the corresponding inputs in the referenced flow's **Start** block. The values that the referenced flow produces will then be available through the **Flow** block's outputs. To learn more, see [The Flow block](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/flow-module/).
The scenarios you created to provide data to the inputs in the referenced flow's **Start** block won't be available to the **Flow** block. This means that in the flow containing the **Flow** block, you need to add blocks or scenarios to supply data to the inputs.
## Example
Suppose you make the following flow:
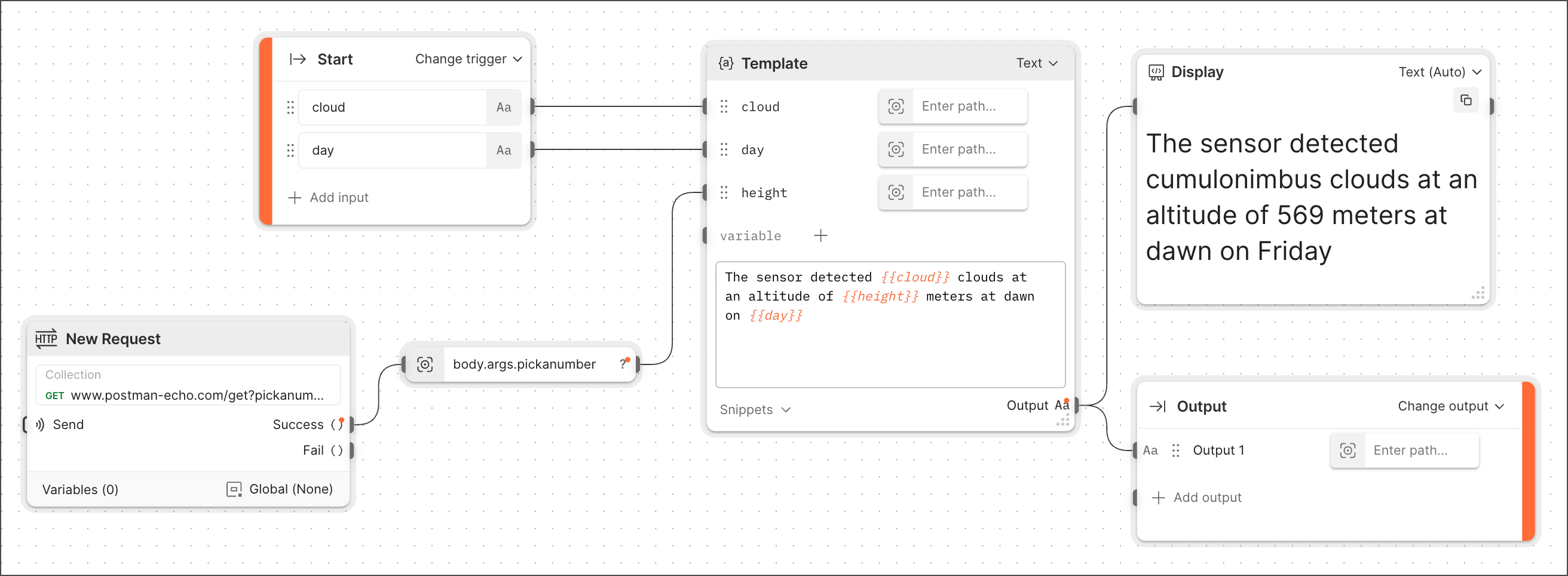 You name the flow **Build wx message** and use a **Flow** block to reference it in another new flow. Encapsulating all the original flow's blocks in a single **Flow** block makes your new flow simpler and easier to understand.
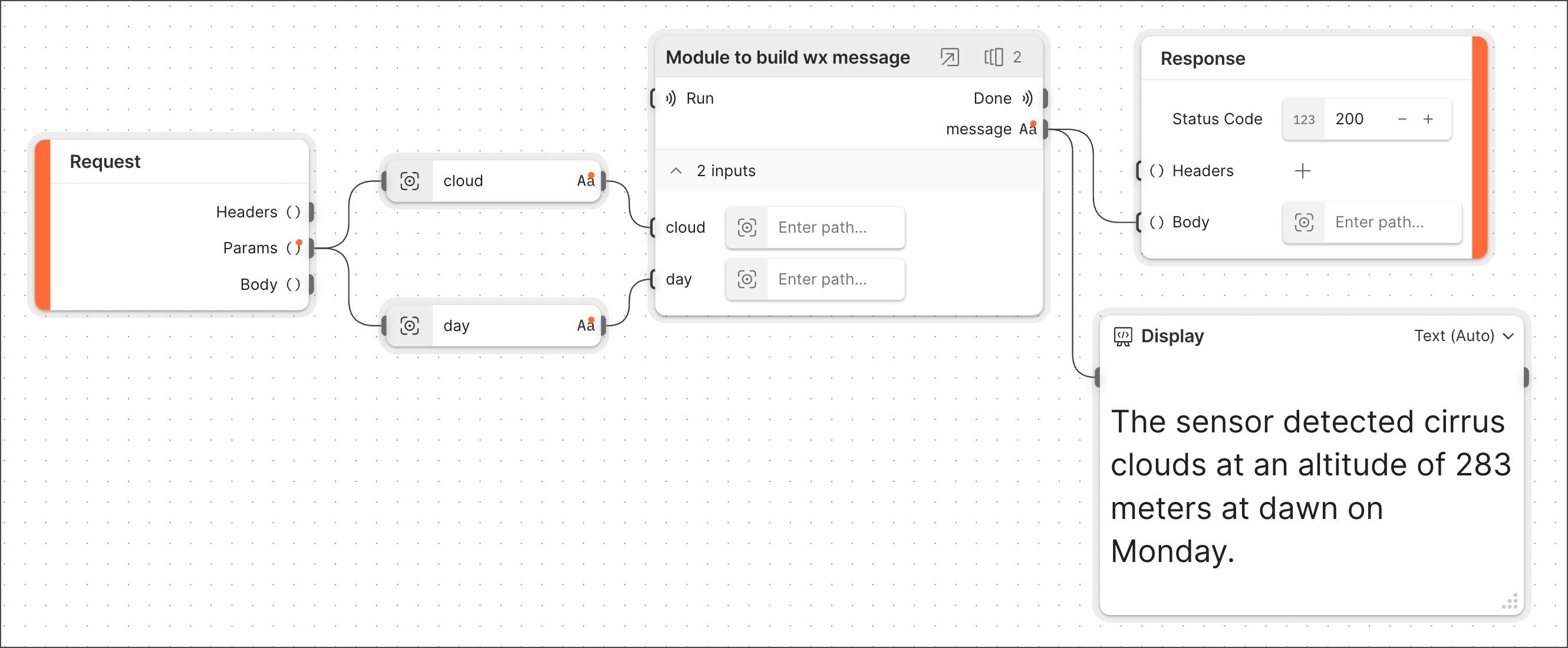
Providing data to the **Flow** block's inputs is required. When testing the new flow, you create a scenario to provide the data. The result looks like this:
You name the flow **Build wx message** and use a **Flow** block to reference it in another new flow. Encapsulating all the original flow's blocks in a single **Flow** block makes your new flow simpler and easier to understand.
Providing data to the **Flow** block's inputs is required. When testing the new flow, you create a scenario to provide the data. The result looks like this:
 ## Related blocks
Upon creation, every flow has a **Start** block. If you add inputs to a **Start** block, they will become inputs in any [**Flow**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/flow-module/) block referencing the flow that contains the **Start** block.
## Related blocks
Upon creation, every flow has a **Start** block. If you add inputs to a **Start** block, they will become inputs in any [**Flow**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/flow-module/) block referencing the flow that contains the **Start** block.
 The **Start** block is automatically added to every new flow. It triggers connected blocks to run, but connecting blocks to the **Start** block is optional. You can add inputs to this block that receive data from [scenarios](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/). You can also change the **Start** block to a [**Request**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/request/) or [**Schedule**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/schedule/) block so you can [deploy](/docs/postman-flows/reference/flows-actions-overview/) the flow to the Postman cloud.
## Inputs
By default, the **Start** block has no input ports. You can [add inputs](#receive-data-with-inputs) as desired. When you add an input to the **Start** block, Postman Flows creates a **Start Trigger** [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/) and adds the inputs to it as key-value pairs. The input's name is the key, and the value is empty until you edit the scenario.
## Output
By default, the **Start** block has a single output port you can connect to other blocks. Any blocks connected to the **Start** block's output port will run when you click the **Run** button. If you add inputs to the **Start** block, each new input will have its own output port that sends data defined in the flow's [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/).
## Setup
The **Start** block appears automatically on every new flow's canvas. A new **Start** block is connected to three buttons you can click to do the following:
*
The **Start** block is automatically added to every new flow. It triggers connected blocks to run, but connecting blocks to the **Start** block is optional. You can add inputs to this block that receive data from [scenarios](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/). You can also change the **Start** block to a [**Request**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/request/) or [**Schedule**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/schedule/) block so you can [deploy](/docs/postman-flows/reference/flows-actions-overview/) the flow to the Postman cloud.
## Inputs
By default, the **Start** block has no input ports. You can [add inputs](#receive-data-with-inputs) as desired. When you add an input to the **Start** block, Postman Flows creates a **Start Trigger** [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/) and adds the inputs to it as key-value pairs. The input's name is the key, and the value is empty until you edit the scenario.
## Output
By default, the **Start** block has a single output port you can connect to other blocks. Any blocks connected to the **Start** block's output port will run when you click the **Run** button. If you add inputs to the **Start** block, each new input will have its own output port that sends data defined in the flow's [scenario](/docs/postman-flows/build-flows/configure/scenarios/).
## Setup
The **Start** block appears automatically on every new flow's canvas. A new **Start** block is connected to three buttons you can click to do the following:
*  You name the flow **Build wx message** and use a **Flow** block to reference it in another new flow. Encapsulating all the original flow's blocks in a single **Flow** block makes your new flow simpler and easier to understand.
Providing data to the **Flow** block's inputs is required. When testing the new flow, you create a scenario to provide the data. The result looks like this:
You name the flow **Build wx message** and use a **Flow** block to reference it in another new flow. Encapsulating all the original flow's blocks in a single **Flow** block makes your new flow simpler and easier to understand.
Providing data to the **Flow** block's inputs is required. When testing the new flow, you create a scenario to provide the data. The result looks like this:
 ## Related blocks
Upon creation, every flow has a **Start** block. If you add inputs to a **Start** block, they will become inputs in any [**Flow**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/flow-module/) block referencing the flow that contains the **Start** block.
## Related blocks
Upon creation, every flow has a **Start** block. If you add inputs to a **Start** block, they will become inputs in any [**Flow**](/docs/postman-flows/reference/blocks/flow-module/) block referencing the flow that contains the **Start** block.