# Create a count-based loop with the Repeat block
You can build a flow that loops over a count. For example, you can run a flow that loops over a count of three and generates a list of three random numbers.
This tutorial's goal is to teach you how to set up and use count-based loops. To achieve this goal, you'll build a flow that uses a loop to count to three.
## Create a new flow
You build flows in a workspace. Workspaces let you organize your API projects and collaborate with your team.
To create a new flow, do the following:
1. Choose an existing workspace or [create a new one](/docs/collaborating-in-postman/using-workspaces/create-workspaces/).
2. In the upper left corner, click **New** >  **Flow**.
## Add a Repeat block
The **Repeat** block lets you build a loop that iterates over a count. For example, to run a loop three times, set the count to three.
In the next procedure, you'll use the **Number** block to define this count.
To add a **Repeat** block, do the following:
1. From the canvas toolbar, click
**Flow**.
## Add a Repeat block
The **Repeat** block lets you build a loop that iterates over a count. For example, to run a loop three times, set the count to three.
In the next procedure, you'll use the **Number** block to define this count.
To add a **Repeat** block, do the following:
1. From the canvas toolbar, click  **Add blocks**.
2. Select
**Add blocks**.
2. Select  **Repeat** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Repeat" in search.
3. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Repeat** block and click that location.
## Connect a Number block
When you connect two blocks, you connect one block's input to another block's output. Inputs are on the block's left side and outputs are on its right side.
In this tutorial, you'll use the **Number** block to define the number of times you want to run your loop.
To connect a **Number** block, do the following:
1. Hover over the **Repeat** block's **Count** input port. The pointer changes to a crosshair.
2. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Number** block and drag the port to that location.
3. Select
**Repeat** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Repeat" in search.
3. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Repeat** block and click that location.
## Connect a Number block
When you connect two blocks, you connect one block's input to another block's output. Inputs are on the block's left side and outputs are on its right side.
In this tutorial, you'll use the **Number** block to define the number of times you want to run your loop.
To connect a **Number** block, do the following:
1. Hover over the **Repeat** block's **Count** input port. The pointer changes to a crosshair.
2. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Number** block and drag the port to that location.
3. Select  **Number** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Number" in search.
4. Enter a whole number. For example, if you want your loop to repeat three times, enter **3**.
## Connect an Evaluate block
Many programming languages start counting with an index value of zero (for example, 0, 1, 2).
In the following steps, you'll use an **Evaluate** block to add one to the count to start counting with an index value of one (for example, 1, 2, 3).
To connect an **Evaluate** block, do the following:
1. Hover over the **Repeat** block's output port. The pointer changes to a crosshair.
2. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Evaluate** block and drag the port to that location.
3. Select
**Number** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Number" in search.
4. Enter a whole number. For example, if you want your loop to repeat three times, enter **3**.
## Connect an Evaluate block
Many programming languages start counting with an index value of zero (for example, 0, 1, 2).
In the following steps, you'll use an **Evaluate** block to add one to the count to start counting with an index value of one (for example, 1, 2, 3).
To connect an **Evaluate** block, do the following:
1. Hover over the **Repeat** block's output port. The pointer changes to a crosshair.
2. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Evaluate** block and drag the port to that location.
3. Select  **Evaluate** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Evaluate" in search.
4. Rename the variable. For example, enter **index**.
5. Add the following to the code editor:
```javascript
index + 1
```
This code takes the index, which starts at zero, and adds one.
Alternatively, use the [Flows Query Language](/docs/postman-flows/flows-query-language/introduction-to-fql/) (FQL) `$now()` function to timestamp the loop. This is another great way to conceptualize what happens when you run a loop.
## Connect a Collect block
The **Collect** block saves multiple outputs to a list. In this tutorial, your loop will run three times, output three values, and use this block to save these values to a list.
To connect a **Collect** block, do the following:
1. Hover over the **Evaluate** block's output port. The pointer changes to a crosshair.
2. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Collect** block and drag the port to that location.
3. Select
**Evaluate** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Evaluate" in search.
4. Rename the variable. For example, enter **index**.
5. Add the following to the code editor:
```javascript
index + 1
```
This code takes the index, which starts at zero, and adds one.
Alternatively, use the [Flows Query Language](/docs/postman-flows/flows-query-language/introduction-to-fql/) (FQL) `$now()` function to timestamp the loop. This is another great way to conceptualize what happens when you run a loop.
## Connect a Collect block
The **Collect** block saves multiple outputs to a list. In this tutorial, your loop will run three times, output three values, and use this block to save these values to a list.
To connect a **Collect** block, do the following:
1. Hover over the **Evaluate** block's output port. The pointer changes to a crosshair.
2. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Collect** block and drag the port to that location.
3. Select  **Collect** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Collect" in search.
## Connect a Display block
The **Display** block displays incoming data, such as the **Collect** block's outgoing list.
To connect a **Display** block, do the following:
1. Hover over the **Collect** block's output port. The pointer changes to a crosshair.
2. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Display** block and drag the port to that location.
3. Select
**Collect** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Collect" in search.
## Connect a Display block
The **Display** block displays incoming data, such as the **Collect** block's outgoing list.
To connect a **Display** block, do the following:
1. Hover over the **Collect** block's output port. The pointer changes to a crosshair.
2. Decide where on the canvas you want to place the **Display** block and drag the port to that location.
3. Select  **Display** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Display" in search.
## Run the flow
From the canvas toolbar, click
**Display** from the list. If you want to search for the block, enter "Display" in search.
## Run the flow
From the canvas toolbar, click  **Run**.
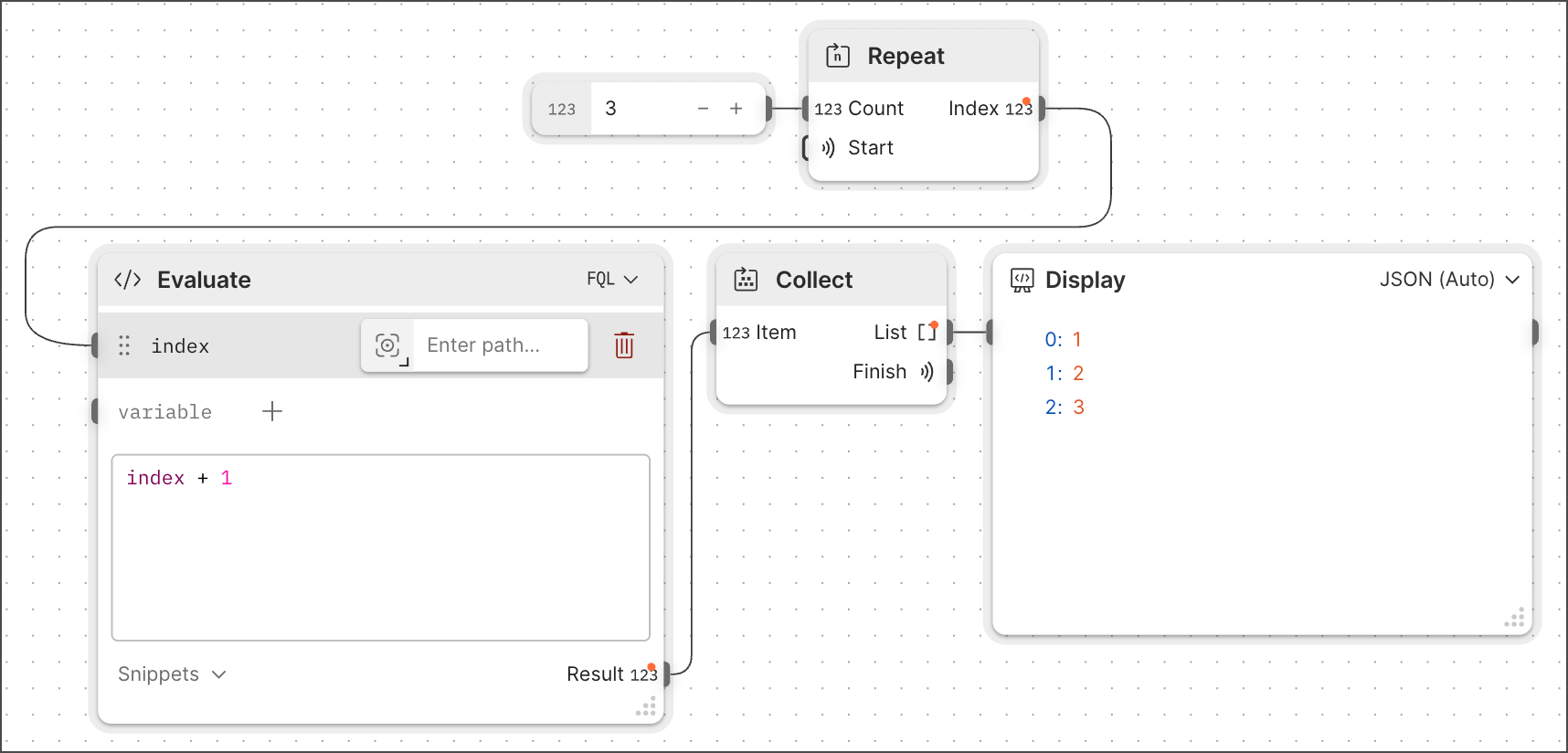
Congratulations! You created a count-based loop and displayed the result in a **Display** block.
**Run**.

Congratulations! You created a count-based loop and displayed the result in a **Display** block.