Access Postman data programmatically
The Postman API enables you to programmatically access data stored in your Postman account. You can use the API to perform actions such as managing your collections, APIs, workspaces, and more.
The access rate limits for your Postman account depend on your Postman plan. For more information, see Postman API rate limits.
This tutorial shows you how to make your first call to the Postman API. You can also learn more about the Postman API by reading the Postman API documentation. There you will find information to help you get started and information about each endpoint and operation.
Get your API key
Before you can use the Postman API, you’ll need an API key. An API key is a way to identify who you are when you make a request to the Postman API endpoints. It also lets the system know what you can do with the Postman API. For more details, see Generate and use Postman API keys.
Store your API key
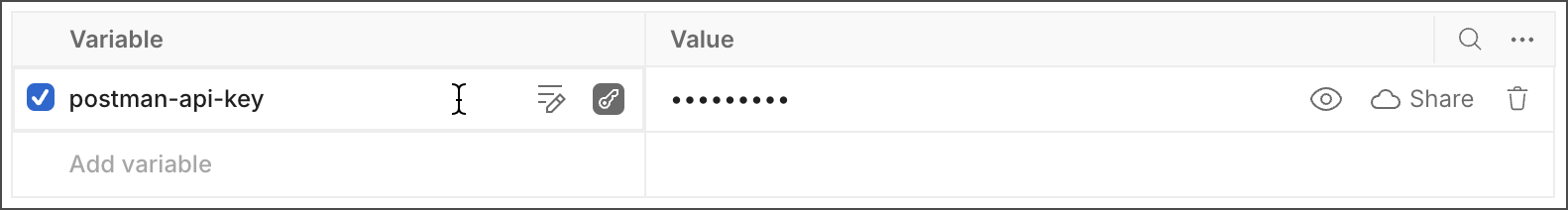
After you create your API key, store it in your Postman Vault as a vault secret. You can then reuse it in your local instance of Postman. Only you can access and use values associated with your vault secrets, and they aren’t synced to the Postman cloud.
If you want to share sensitive data with collaborators, you can store it in an environment and set the environment variable as sensitive data. Make sure you follow these security best practices:
-
Store your API key as a variable set as sensitive data.
-
Store your API key as a local value so you don’t share it with other team members.
Make your first request
For your first request, you’ll use the /me endpoint. This is a basic GET endpoint that doesn’t change any data. It returns information about the user that owns the API key that’s being used to authenticate the call.
Fork the Postman API collection
Before you call the /me endpoint, fork the Postman API collection. Forking creates a copy of the collection that you can change but doesn’t affect the parent element.
To fork the collection, click Run in Postman:
Follow the prompts. Enter a label for your forked Postman API collection in the Fork label box. Then in the Workspace box, select the workspace in which to create the forked collection.
Click Fork Collection to create the fork. Postman redirects you to the workspace you selected to create the forked Postman API collection.
Make the API call
-
In the forked Postman API collection, select the Users folder. This folder contains the Get authenticated user (
/me) endpoint. -
Select the Get authenticated user request, then click Send. Postman returns an HTTP
401 Unauthorizedresponse. This is because the endpoint requires authorization before it returns information about the API key’s owner.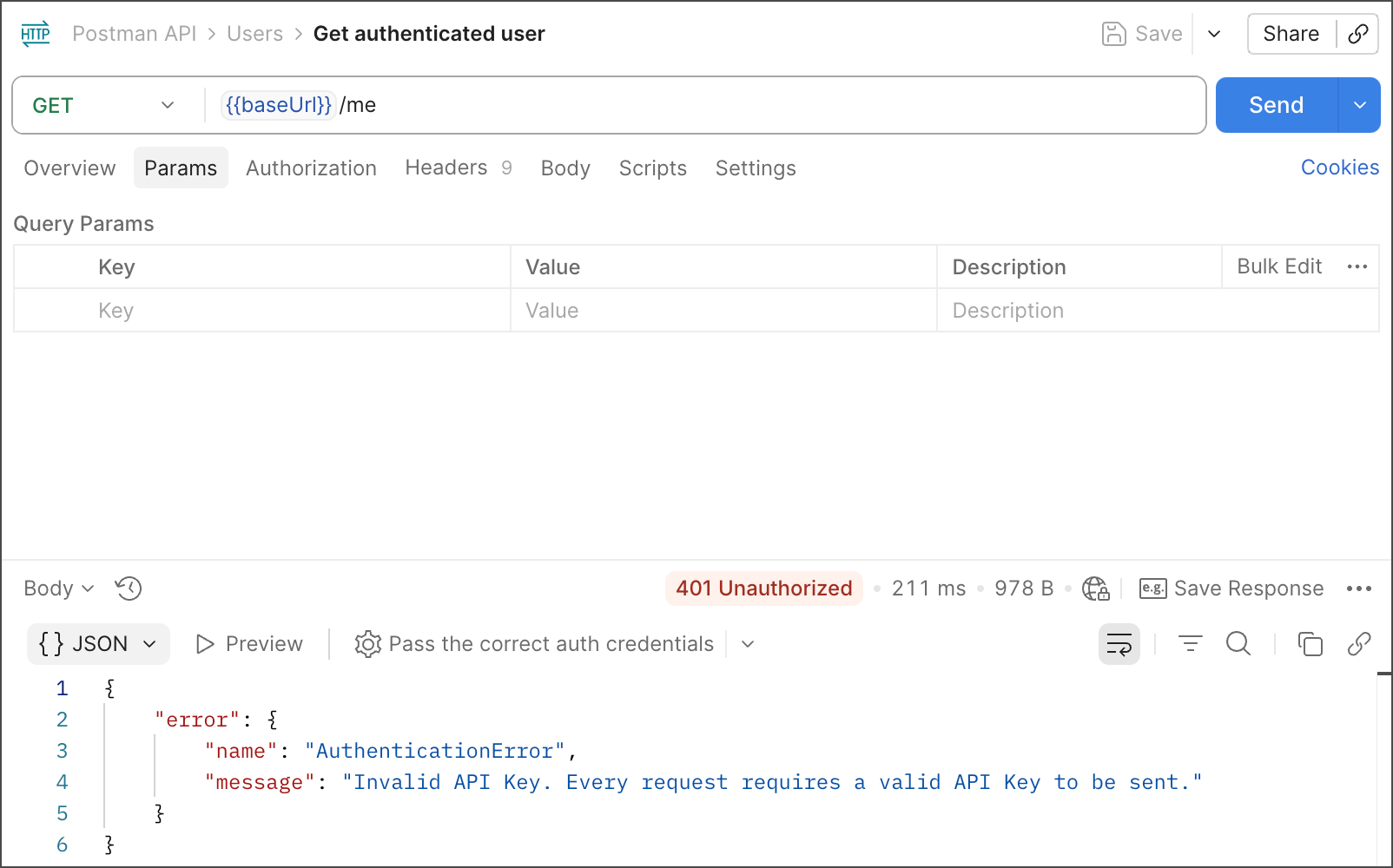
-
Use the API key that you stored in your Postman environment. To do this, select the environment where you stored your API key.
-
Click Send. The Postman API returns a successful response.
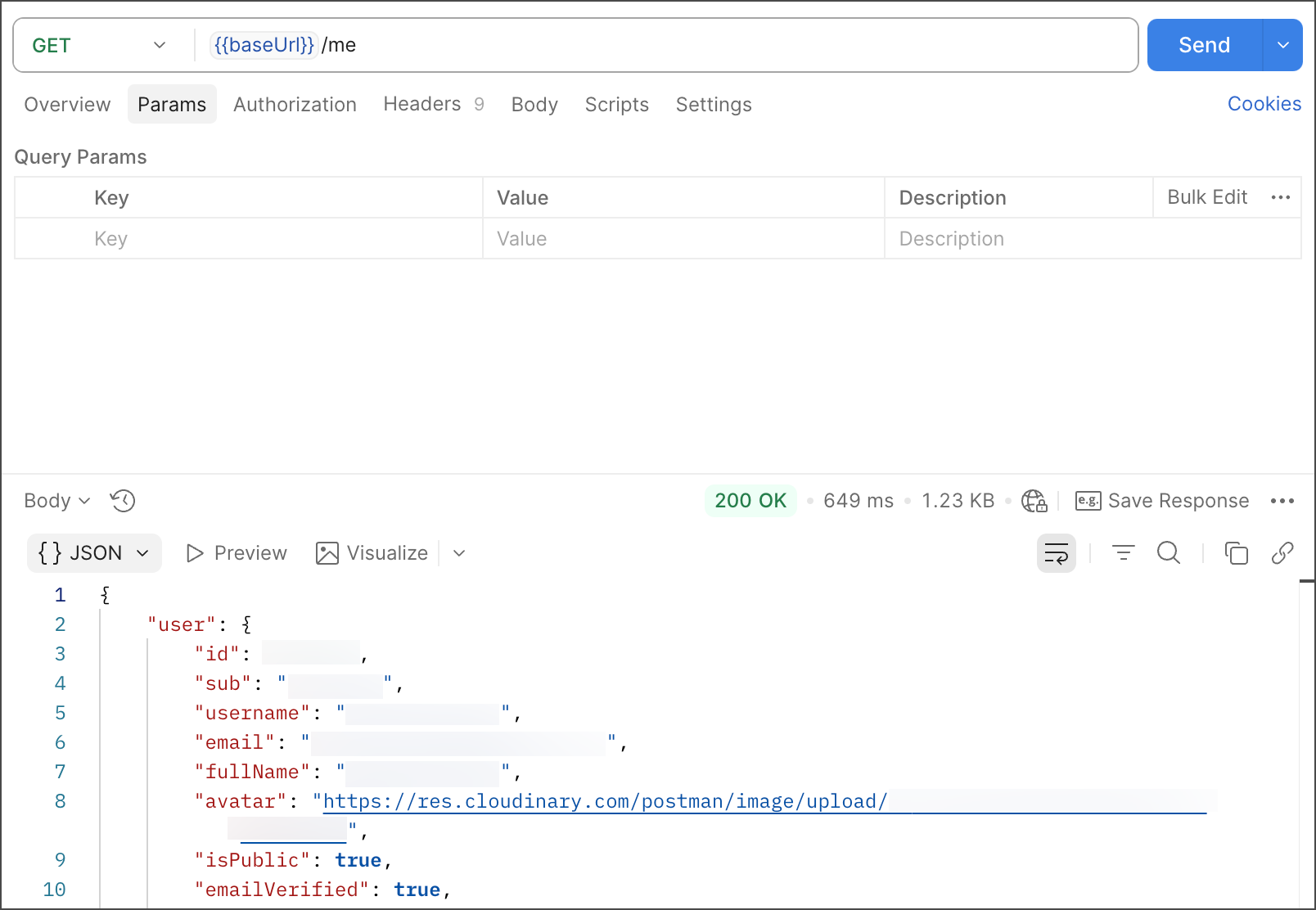
Congratulations! You have made your first call to the Postman API.