Configure runners for internal APIs
This feature is available on Postman Enterprise plans. For more information, see the pricing page.
As an Admin or Super Admin, you can use Private API Monitoring to create a runner that monitors and tests your organization’s APIs from your internal network, without publicly exposing your endpoints. You can create a runner when you configure a monitor. You can also create a runner from Runner settings.
You can start the runner with the Postman CLI command from your internal network and securely poll Postman for monitor runs. Once you set up the runner in your internal network, your teammates can select the runner when creating monitors. You can check the monitor results in Postman to learn about your monitor’s performance.
Create a runner when you configure a monitor
As an Admin, you can create a new runner when you configure a monitor. Runners created this way are visible in all your team’s internal workspaces.
To create a runner when you configure a monitor, do the following:
-
Under Runners, select Manually Select then click
Add Runner.
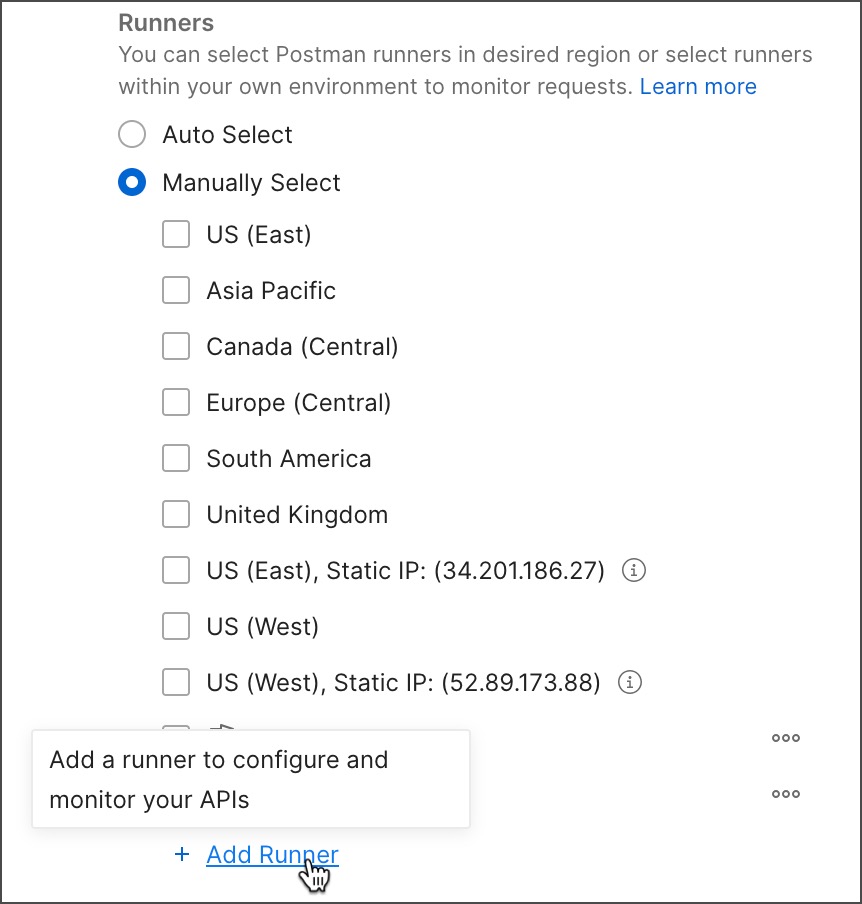
-
Give your runner a name and description.
-
Click Next: Install Runner.
-
Click
Copy to clipboard to copy the Postman CLI
runnercommand with the runner ID and key.You can’t access the runner key again later. You can reset the runner key later, if needed.
-
Click Done.
Create a runner from Runner settings
As an Admin, you can create a new runner from Runner settings.
To create a runner from Runner settings, do the following:
-
Click your profile icon in the upper right corner.
-
Hover over your team and click
Organization settings.
-
Click Runners in the left sidebar.
-
Click Add Runner in the upper right of Runner settings.
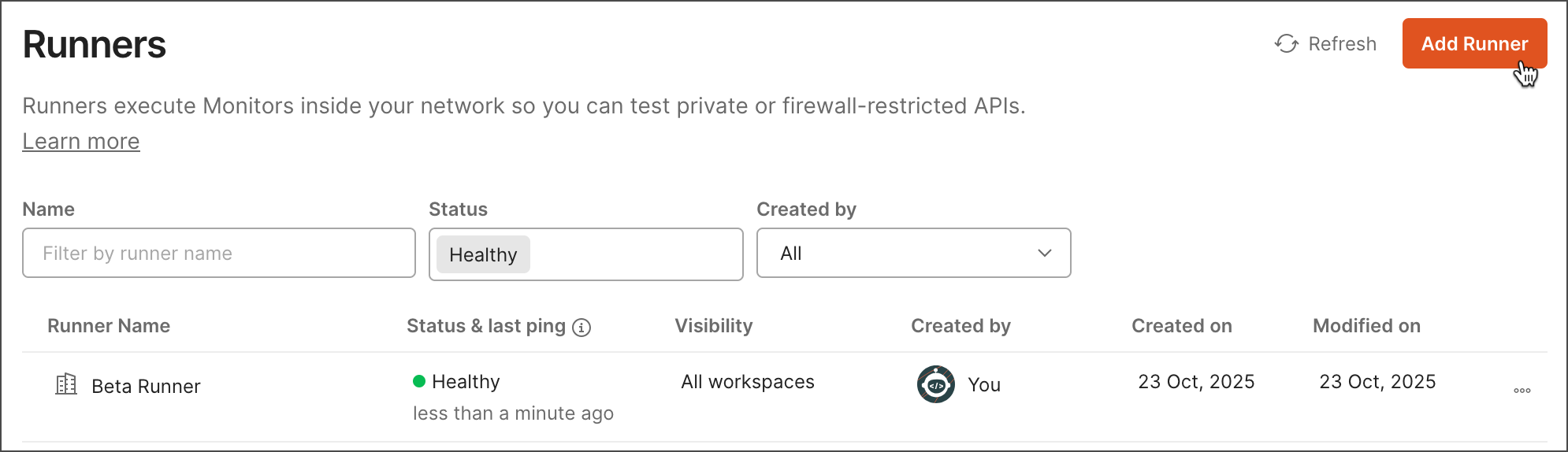
-
Give your runner a name and description.
-
Choose internal workspaces where the runner is visible. Select one of the following:
-
All internal workspaces in team - The runner is visible in all internal workspaces in your team.
-
Selected workspace - Click the Select workspace dropdown list and then select the internal workspace where the runner is visible.
You can change this later when you’re ready to make the runner visible in all your team’s internal workspaces.
-
-
Click Next: Install Runner.
-
Click
Copy to clipboard to copy the Postman CLI
runnercommand with the runner ID and key. Postman identifies a runner using its runner ID, and a runner uses the runner ID and key to authenticate with Postman.You can’t access the runner key again later. You can reset the runner key later, if needed.
-
Click Done.
Learn how to manage your runners from Runner settings.
Set up a runner with the Postman CLI
You can get started by learning how to start the runner in your internal network. You can containerize the runner using Docker to set up the runner in your cloud network, like a virtual private cloud. Learn more about setting up the runner with the Postman CLI.
Once the runner is set up and running, your teammates can select the runner when creating a monitor.
Your Postman plan gives you a limited number of requests that can be run by your Postman Monitors each month. Requests run by Private API Monitoring count toward this same limit. Learn more about resource usage in Postman.
Select the runner when creating a monitor
When creating a monitor, select a runner to run in your internal network. Runners are only supported in internal workspaces. After you’ve created the monitor with the runner, you can check your monitor’s results in Postman.
To create a monitor that uses an existing runner, do the following
- Create or edit a monitor.
- Under Run this monitor, specify how often Postman runs the selected monitor. This can be as often as every five minutes for a status page, or a basic check once a week on your endpoints.
- Under Runners, select Manually Select then select a runner.
- Continue configuring your monitor.
- Click Create Monitor.
Check your internal API monitor
Your monitor’s results show the health and performance of your internal APIs. For more information about Postman Monitor features, see View monitor results.