The HTTP Request block
The HTTP Request block runs an HTTP request that you select from a collection and sends the result from its output port.
The HTTP Request block consumes one credit each time it runs. To learn more, see How Flows consume credits.
Input
Send - If you connect another block to this input port, that block triggers the HTTP Request block to run. This connection is optional. The HTTP Request block will run when the flow runs, even if this port isn’t connected to another block.
Variables - If the selected request obtains values from variables, those variables will be listed here. Requests can use variables to set values for query parameters and for elements of the request body.
To learn how to set or override these variable values, see Setup.
When a request is created in a collection, if a query parameter’s value was set without using a variable:
-
No variable will be listed for it in the HTTP Request block.
-
There is no way to override its value from a flow.
Outputs
Success - Sends the response of a successful API request. To succeed, a request must return a 2xx HTTP status code and pass all of its tests.
Fail - Sends the response of an unsuccessful API request. A request will fail if it returns an HTTP status code other than 2xx or if any of its tests fail. If your request is returning a 2xx HTTP status code but failing a test, you might want to disregard the test temporarily. In this case, you can connect a block to the Fail output and that block will receive the data returned by the request.
Setup
Find or create new request - Click to open a dropdown list showing all the collections in your workspace. Select a collection, then select a request or Create a new request. If there are no collections in the workspace, some introductory requests will appear that you can choose from to get started.
Variables - To assign a value to a variable, use either of the following methods:
-
Connect another block’s output port to the variable’s input port.
-
Click
Add data blocks to Insert a data block inline.
You can also use these value assignment methods if your request obtains values using environment variables or dynamic variables.
-
If your request uses environment variables, corresponding variables will appear in the HTTP Request block. You can select the environment from the
Add environment dropdown list. If you can’t or don’t want to use the relevant environment, re-create the desired values using one of the value assignment methods.
-
If your request uses dynamic variables, the dynamic variables will work as usual in your flow. If you want to override their values, use one of the value assignment methods to assign the values you prefer.
Here’s an example showing different ways that query parameters can obtain their values:
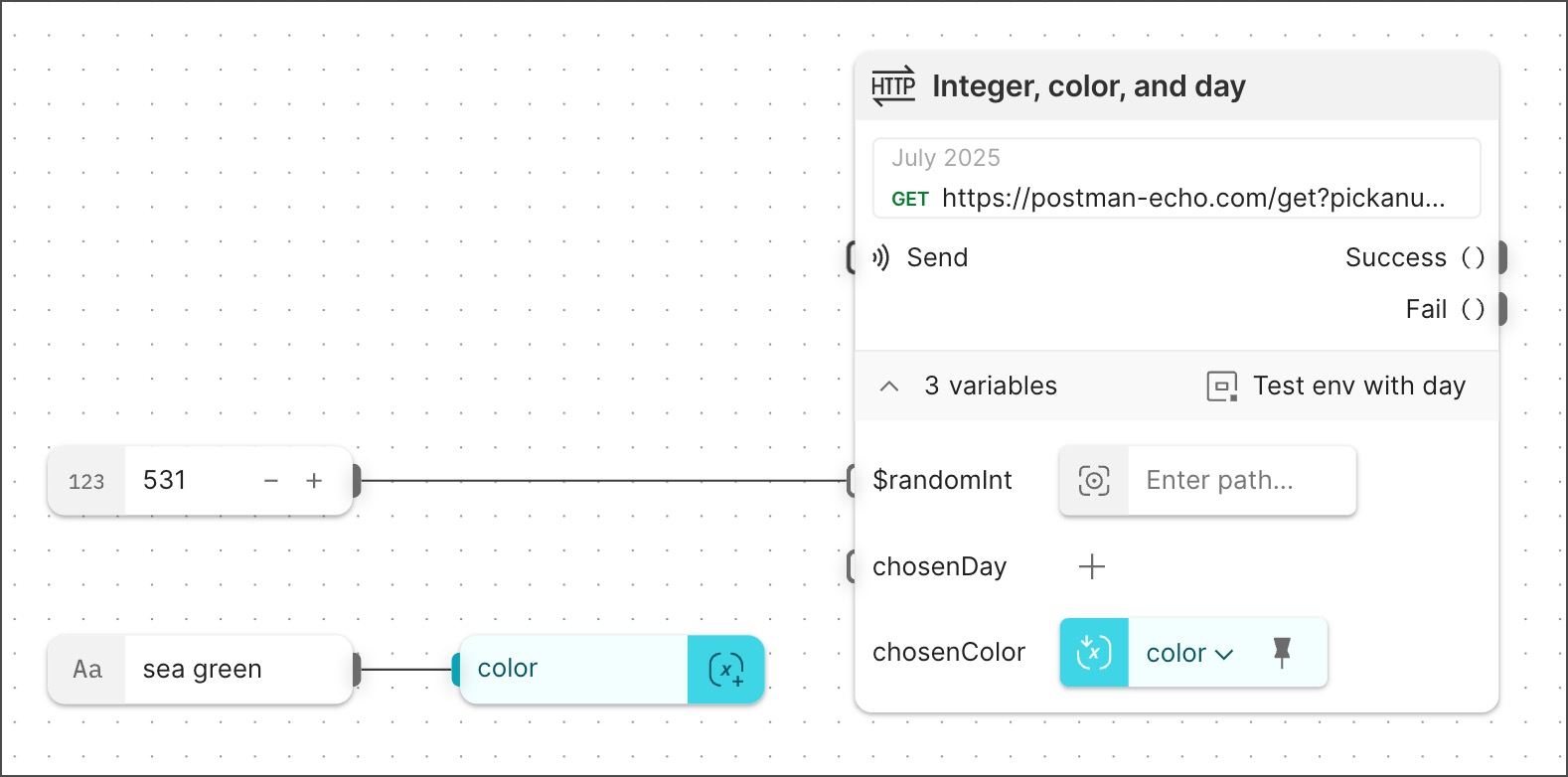
In the example, the request URL is:
The query parameters obtain their values as follows:
-
pickanumberwould get its value from the dynamic variable{{$randomInt}}, but the connected Number block overrides it with the value 531. -
pickacolorgets its value from the variable{{chosenColor}}in an inline Get Variable block that references a Create Variable block. That Create Variable block gets its value (sea green) from a connected String block. -
pickadaygets its value (Tuesday) from the environment variable{{chosenDay}}that’s set in the selected environmentTest env with day.
This example shows how a flow stores and retrieves values with Create Variable and Get Variable blocks. You can also store values as configurations and retrieve them with Get Configuration blocks.
Create a new request
To create new and edit existing requests, you can use the Postman Flows request editor that’s built into the HTTP Request block. To create a request in the HTTP Request block, do the following:
-
Click Find or create new request to open a dropdown list showing the collections in your workspace.
-
Select a collection and click Create a new request. If you don’t have any collections, click Create a new request. The Postman Flows request editor opens.

-
In the request editor, select a method from the dropdown list and enter a URL. Alternatively, you can copy a cURL command from your terminal and paste it here. Besides the URL, this add the parameters, headers, and body specified in your cURL command.
-
(Optional) Select and edit the request’s name.
-
(Optional) Select and edit the request’s parameters, headers, and body.
-
Click Save.
Specify how to parse the response
The HTTP Request block can parse its response as JSON, XML, HTML, or text. By default, the HTTP Request block decides how to parse the response.
To choose your preferred way to parse the response, do the following:
-
Click the HTTP Request block.
-
Click
Additional Settings.
-
Next to
Parse Response, click Auto to view the dropdown list of formats.
-
Select a format from the dropdown list.
Update environment variables with scripts
Requests can change environment variables’ values with scripts. You can configure the HTTP Request block so that environment variable values changed by pre-request and post-request scripts persist or reset when the block’s run completes. By default, script-changed values persist in new HTTP Request blocks. Deployed flows don’t support persistent changed values for environment variables.
To turn persistent changes to environment variables on or off, do the following:
-
Click the HTTP Request block.
-
Click
Additional Settings.
-
Next to Allow persistent changes to environment values, turn the toggle on or off.
 Left is off,
Left is off,  right is on.
right is on. -
Select a format from the dropdown list.
Example
To see the HTTP Request block in an example flow, check out Flow Snippets: HTTP Request.
Related blocks
The Select and Evaluate blocks are often connected to the HTTP Request block. The Select block is useful for extracting specific information from a response. The Evaluate block is useful for transforming response data and creating conditions to route data in your flow based on a response.
Related pages
For tutorials that use the HTTP Request block, see the following: