Test your API using the Collection Runner
Send some or all of the API requests in a Postman Collection in the order you choose with the Collection Runner. The Collection Runner logs the test results for each request, and it can use scripts to pass data between requests and change the request workflow.
Use collection runs to automate your functional API testing. You can run collections manually, or schedule collection runs in the Postman cloud with the Collection Runner or monitors. You can also integrate collection runs with your CI/CD pipeline using the Postman CLI, Postman’s command line tool.
Configure a collection run
You can manually run the requests in a collection or a folder.
-
Click Collections in the sidebar and select the collection or folder you want to run.
You can also run a collection or folder that’s linked to an API. Learn more about adding a collection to an API.
-
Click
Run.

You can also click
Runner from the Postman footer. Drag a collection from the sidebar into the Collection Runner. Or click start with a template to create a new collection with example tests you can run.
-
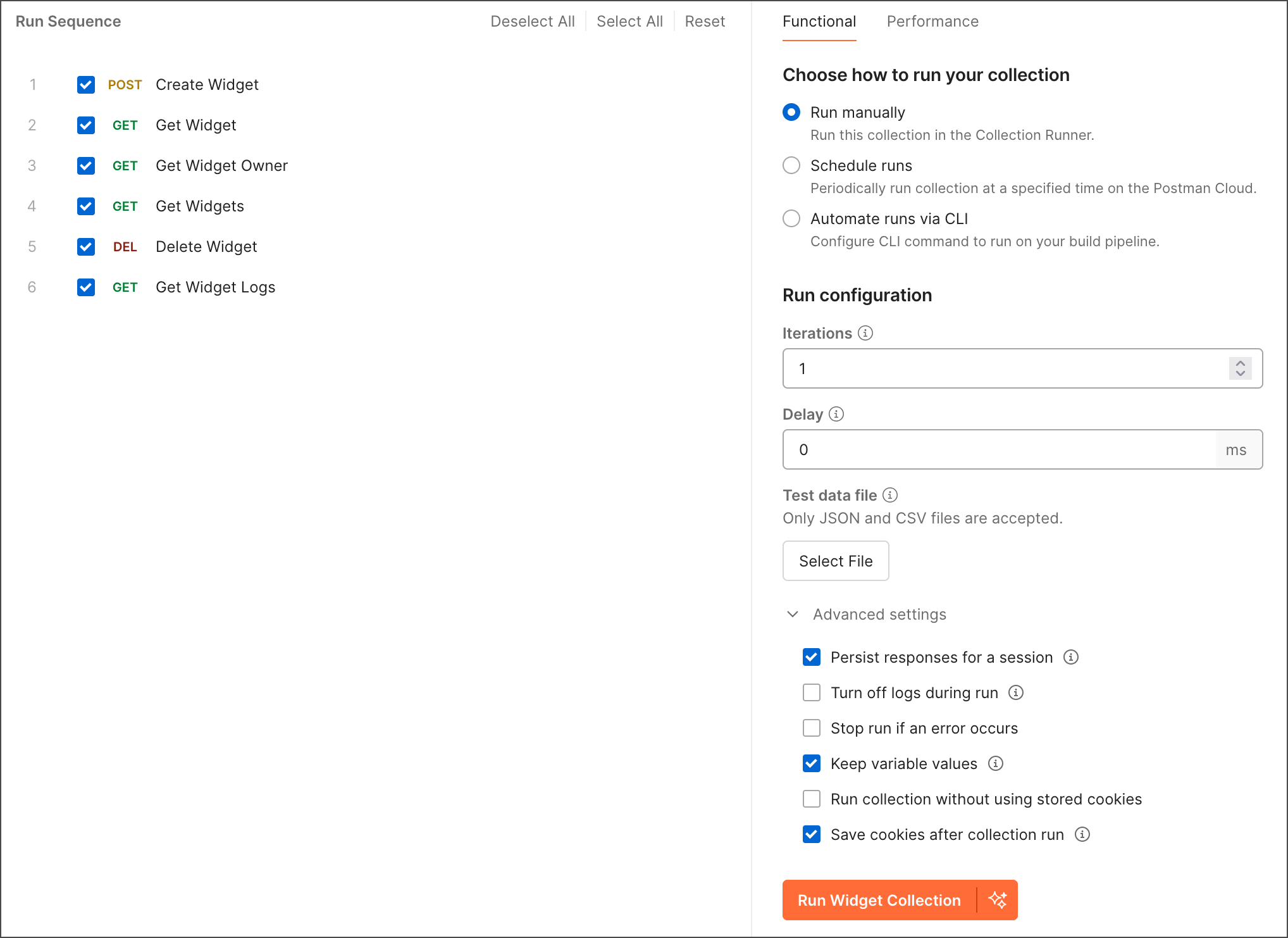
On the Functional tab, click Run manually.
You can also schedule runs and automate runs with the Postman CLI.
-
If you want your collection to run with an environment, select it using the environment selector at the upper right of Postman. You can also click Environments in the sidebar, then select the environment you want to use.
-
Choose any configuration options:
- Iterations - The number of times to run the collection. You can also run collections multiple times with different data sets to build workflows.
- Delay - An interval delay before each request, in milliseconds.
- Test data file - Upload or select an existing data file for the collection run. You can select a data file that was previously uploaded, or you can select a local data file.
- Advanced settings
-
Persist responses for a session - By default, response headers and bodies are persisted so you can review them after running the collection. Request and response bodies are persisted only if they’re less than 300 KB in size.
Your browser or computer may not have enough memory available to persist responses for large collection runs. It’s recommended that you use the Postman desktop app to store a larger amount of request and response data using your computer’s disk space. Learn how to troubleshoot a large collection run.
Request and response details are persisted locally during your current Postman session and aren’t saved permanently. Signing out of Postman, signing into another device with the same account, or refreshing your browser will end your session and remove the logged data.
Response and request details are available for the user who started the collection run. Other team members can’t view details for collection runs that you start.
-
Turn off logs during run - Turn off logging to the Postman Console during the collection run. Request and response details such as method, URL, headers, and body won’t be logged to the Postman Console. Also, all log statements in scripts will be ignored. Selecting this option may improve performance of the Postman app during large collection runs. You can still view request and response details from the run results.
-
Stop run if an error occurs - By default, the collection run stops if an exception is encountered within a script or if there’s a problem sending a request. Clear this checkbox if you want the collection run to continue after an error occurs.
-
Keep variable values - Persist the variables used in the run, so that any variables updated by the run will remain changed after it completes. If you don’t persist variables, changes aren’t saved after the run completes.
Persisting variables in the collection run will update the local value and not the shared value of variables.
-
Run collection without using stored cookies - If your requests use cookies, you can optionally deactivate them for a collection run.
-
Save cookies after collection run - Save the cookies used in this session to the cookie manager. Any values changed by requests during the run will remain after it completes.
-
-
By default, your requests run in the sequence they’re listed in the collection. If you need to change the order in which the requests run, select and drag a request to its new location in the order. You can remove an individual request from the run by clearing the checkbox next to its name. You can also press Shift and then click a range of requests’ checkboxes to add or remove them from the collection run.
You can change the order of requests during a collection run from your request scripts using the
pm.execution.setNextRequest()function. To learn more, see Customize request order in a collection run. -
When you’ve completed your configuration, click Run (collection name).
To run the collection with Postman Agent Mode, click
and then select a suggested task from the dropdown list. For example, select
Add tests based on the response for Agent Mode to run the collection and then suggest tests based on the run results.
Your Postman plan gives you a limited number of collection runs you can use each month. This limit applies to collections that you run in a workspace using the Run manually option, but it doesn’t apply to scheduled collection runs in the Postman cloud. A collection run with multiple iterations counts as a single run.
A message will display in the Collection Runner when you’re approaching your usage limit. Learn more about resource usage in Postman.
Debug run results
When running collections manually, Postman displays the results of your request runs in real time. This includes test results, errors, and any failed test assertions. You can view the source of the collection run, selected environment, number of iterations, total duration, number of tests, number of errors, and average response time.
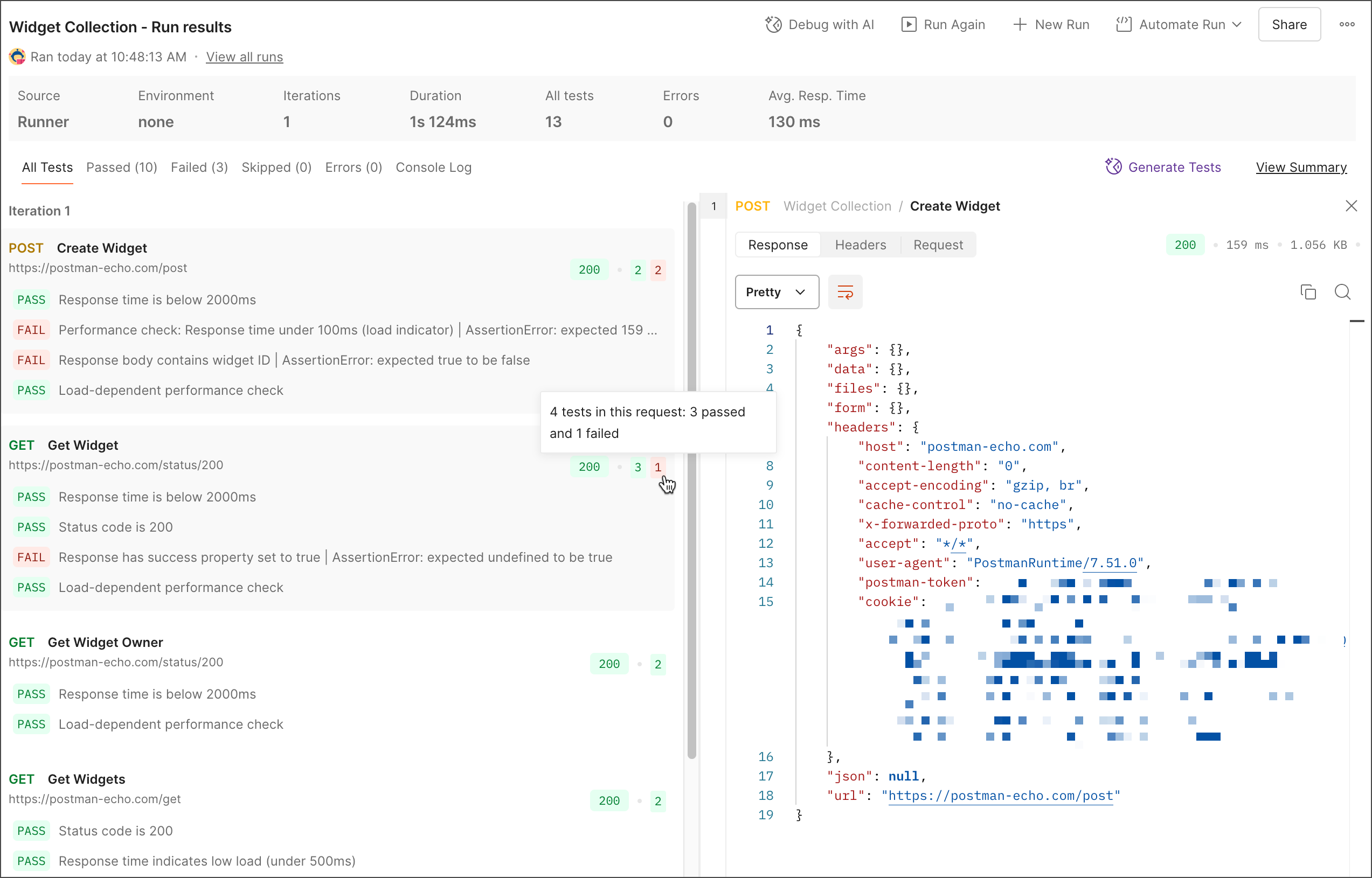
To learn more about what happened during the collection run, do any of the following:
Test results
-
Click anywhere in the run results page and scroll through the list with the following keys and keyboard shortcuts:
-
Click a request to view details about the request. You can view general information about the request and the request headers and body. You can also view the response headers and body if the Persist responses for a session checkbox was selected when configuring the collection run.
-
Click the name of a request to open the request in a new tab. You can view any post-response scripts or click Send to send the request again.
-
If your requests are in a folder, click the name of the folder to open it in a new tab.
-
If your collection run included more than one iteration, click an iteration number to jump to the results of a specific iteration.
-
Hover over the response status code next to a request to show the full status code and a description.
-
Click the Console Log tab to view script-level console messages grouped by request. Badges identify each message as a log, info, warning, or error message.
-
If your collection run included more than one iteration, click an iteration number to jump to the results of a specific iteration.
-
Click View all runs to view a list of past runs. Learn more about viewing run history.
-
Click View Summary to view a summary of the collection run, including test results. To return to the full results, click View Results.
You can use Postman Agent Mode to debug the run results and generate tests for requests in your collection:
- If any of your requests encounter a failure or error, you can click
Debug with AI to use Agent Mode to help you debug and fix them.
- If any of your requests are missing tests, you can click
Generate Tests to use Agent Mode to suggest test assertions.
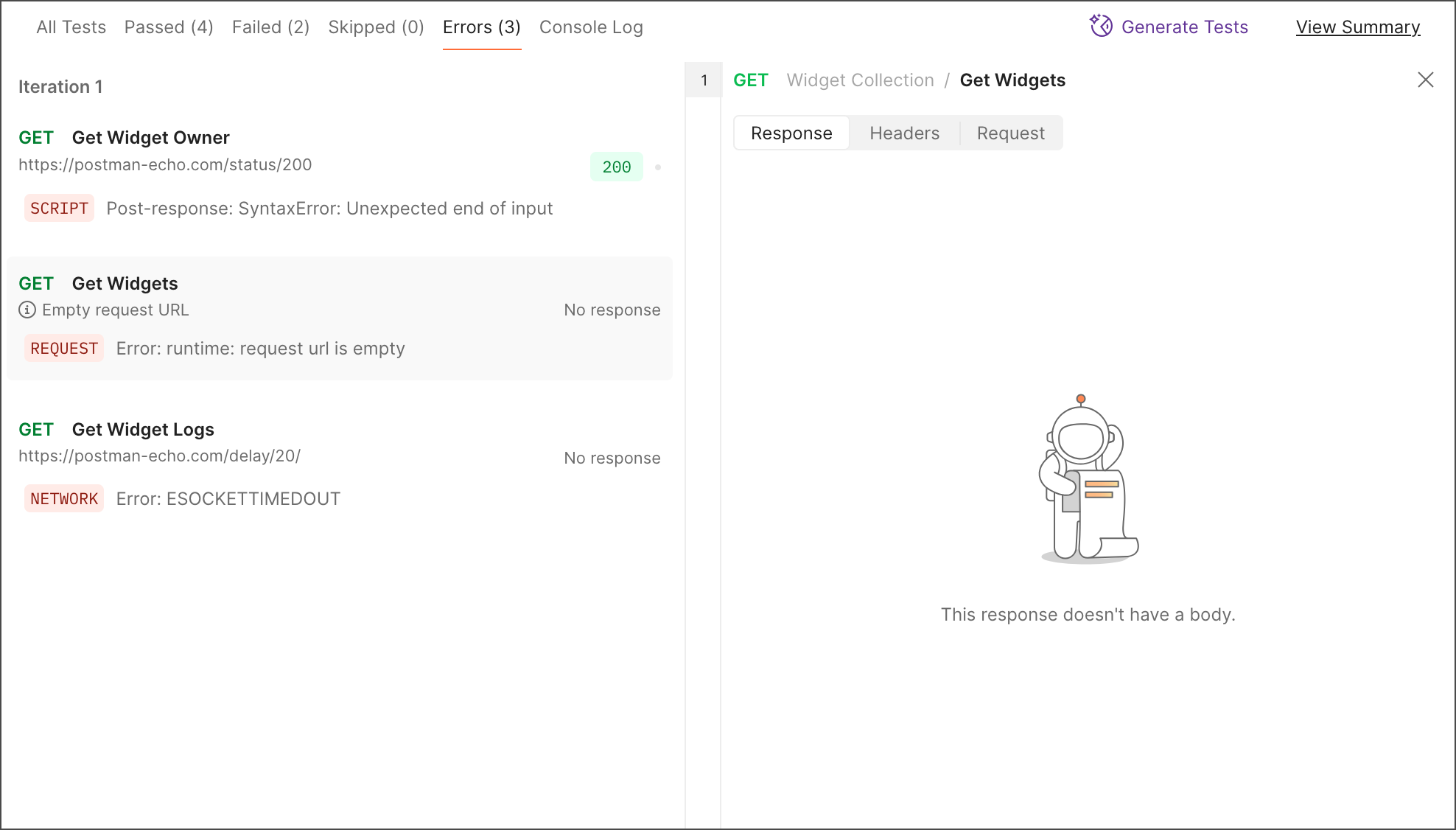
Errors
-
Click the Errors tab to filter results by requests that encountered errors. Note that errors indicate runtime issues like timeout or TLS handshake errors. Failed requests occur when one or more user-specified checks (like post-request scripts) don’t match expectations.
-
The requests in your collection run that have errors appear in the run results page with an error badge and the error message. Badges identify errors as related to NETWORK, REQUEST, or SCRIPT issues.
Sharing and commenting
-
Click Share in the upper right to share the results with another team member. This provides a link you can give to other team members to view the details of this run. You can also click
Invite people to invite teammates to your workspace. If you’re in an internal workspace only you can access, you can click Invite people to invite teammates to your workspace and then share the results.
-
Click
Comments in the right sidebar and enter your comment. Click Comment to share your comment with your team. Learn more about adding comments.
Delete a collection run
To delete a collection run, click View more actions in the upper right and click
Delete. Click Delete to confirm.
You can run collections with scripts that import packages from your team’s Postman Package Library. Learn how to add packages to the package library, and import packages into your scripts. You can also run collections that import external packages from npm or JSR package registries.
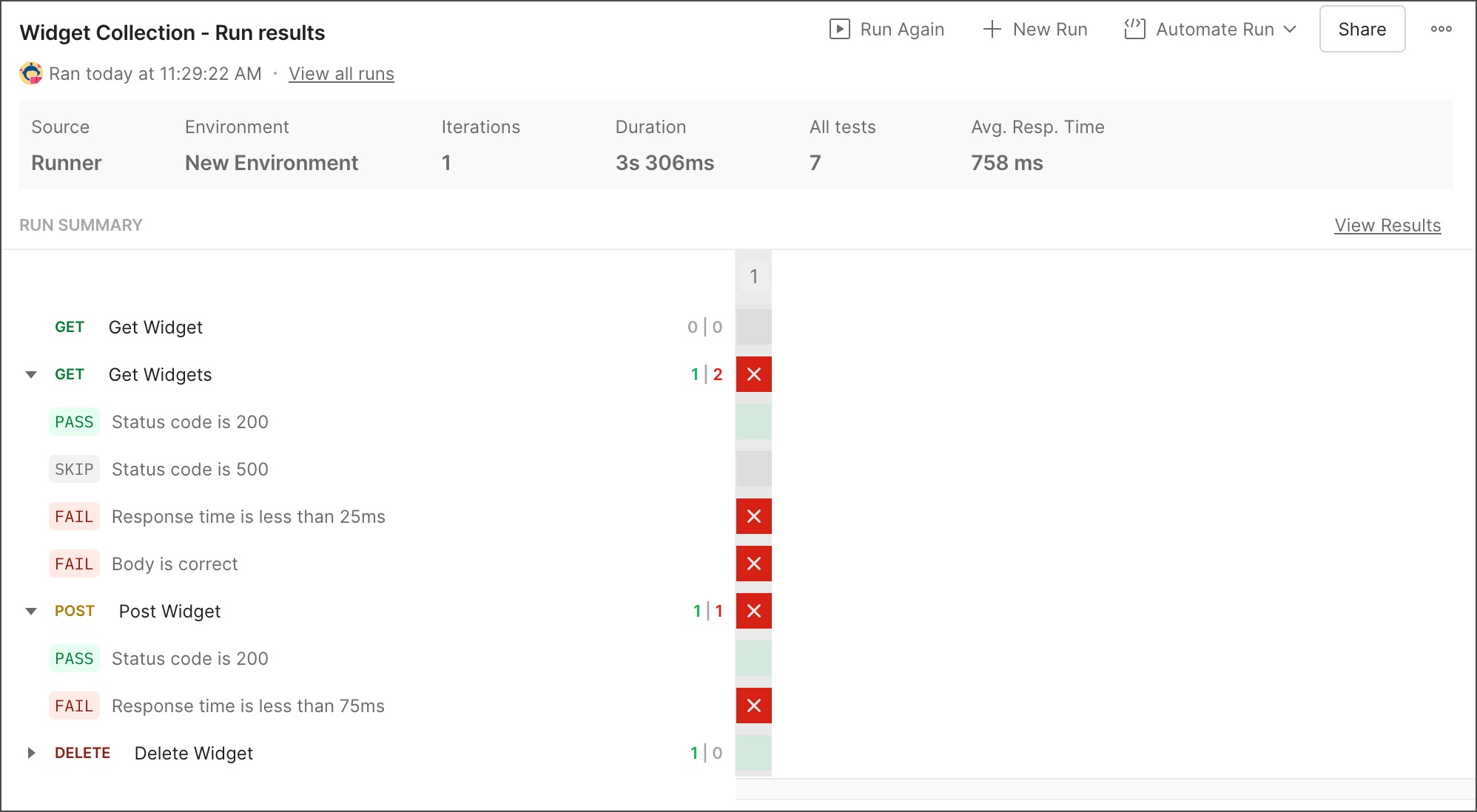
Run the collection again
After reviewing the results of the collection run, you can run the collection again. For example, you can edit the code for a failed test and run the collection again to check if the test succeeds.
To run the collection again from the run results, do one of the following:
- Click
Run Again to run the collection again using the same settings.
- Click
New Run to configure a new run for the collection. Make changes to any settings, and then select Run (collection name) to run the collection again.
- Click
Automate Run to automate runs for the collection. You can schedule a run, run using the Postman CLI, or integrate runs with your CI/CD pipeline.
If you changed the selection or order of requests, or any other settings, the custom order and configuration are saved with the run results.
To run the collection again later using your custom configuration, select the Runs tab in the collection to view past runs. Click View Report next to a run to open the collection run results. From here you can click
Run Again to run the collection again using the same settings.
Troubleshoot large collection runs
A collection run may be large if it has many requests, its requests and responses are large in size, or the number of its iterations is high. Your browser or computer may run out of memory during large collection runs, reducing the performance of your collection runs.
You may be able to use the Postman web app for large collection runs with some configuration changes. For improved performance, it’s recommended that you use the Postman desktop app for large collection runs. The Postman desktop app uses your computer’s disk space, making more memory available during larger collection runs.
If you’re using the Postman web app with large collection runs, you can take the following actions to make more memory available in your browser and improve the performance of your collection runs:
- Deselect the Persist responses for a session checkbox when configuring the collection run.
- Select the Turn off logs during run checkbox when configuring the collection run.
If you’re using the Postman desktop app with large collection runs, you can take the following actions to make more memory available in your computer and improve the performance of your collection runs:
- Deselect the Persist responses for a session checkbox when configuring the collection run.
- Clear your local data and restart Postman. Open the Postman desktop app, click Help in your computer’s menu bar, then click Clear Cache and Reload.
- Free up disk space on your computer.
- Select the Turn off logs during run checkbox when configuring the collection run.
- If the collection run has many requests, break up the requests into multiple smaller collections and run them separately.
- Reduce the number of iterations for the collection run when configuring the collection run.
When using the Postman desktop app during a large collection run, you may be unable to persist responses if your computer runs out of memory during the collection run. Postman may delete responses persisted earlier to create space for new persisted responses. You’ll be notified from the run results if memory was exhausted during the collection run. You can click Retry Run in the notification to run the collection again using the same settings.
For more help troubleshooting a large collection run, contact Postman support with log files attached to your request. Learn how to locate Postman logs.
Export collection runs
You can share collection run results with others by exporting the results from the Collection Runner.
The option to export a collection run report is available in the Postman desktop app but not in the Postman web app.
To export a collection run, do the following:
- Open the collection run in the Collection Runner. You can also access the collection run using History in the sidebar if you don’t have the run open.
- Click
View more actions in the upper right and click
Export Results to download the collection run.
- Choose a location to save your downloaded collection run, then click Save.
You can import the results of a collection run that was exported to a file. Click Runner from the Postman footer and drag the exported file into the Collection Runner.
View run history
Each collection has a Runs tab you can use to view past functional runs, scheduled runs, and performance runs. You can also view details such as test counts and average response times.
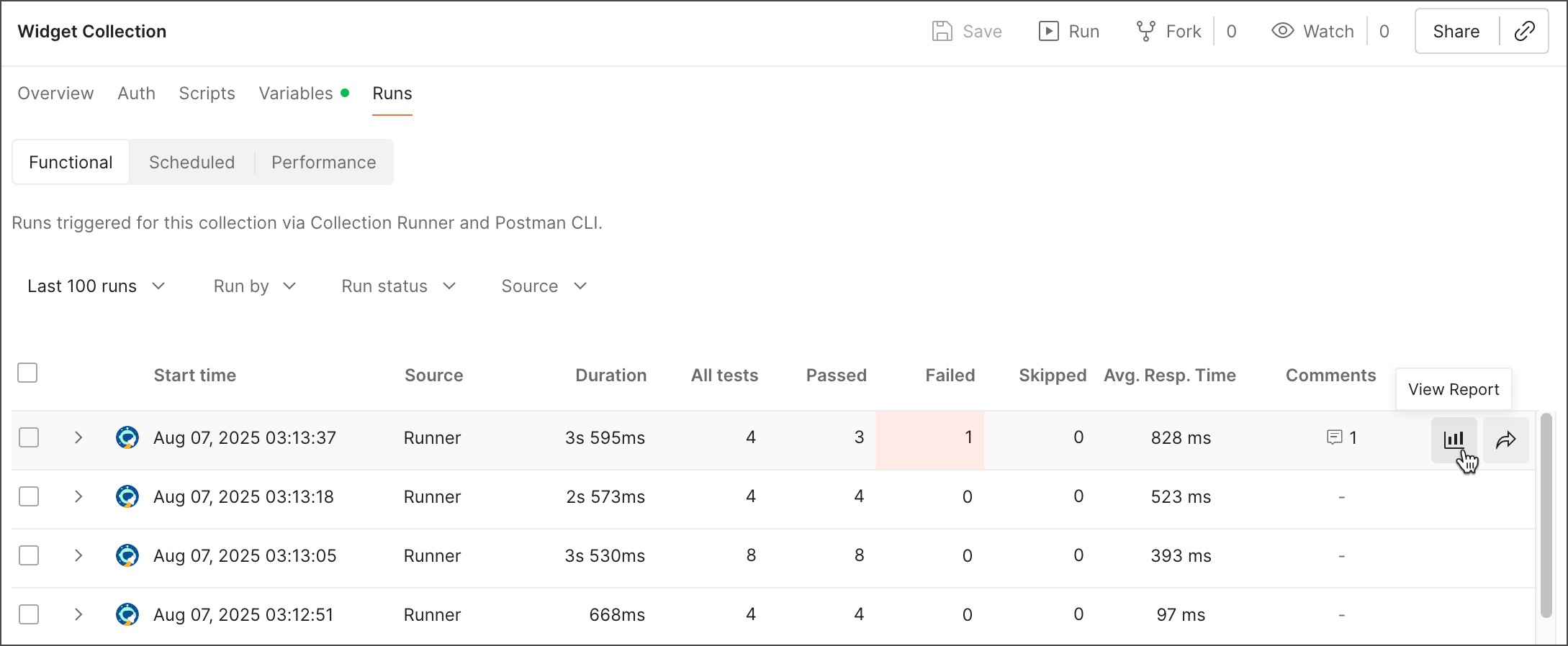
View past runs
The Functional tab has controls to select how many recent collection runs to view. You can filter the displayed runs by user, by run status, and by source (Collection Runner or Postman CLI).
The following are displayed for each collection run:
- A checkbox for each run and an option to select all runs. Select one or more collection runs and click Delete to remove them.
- The start time of the collection run.
- The run source, duration, all tests, passed tests, failed tests, skipped tests, and the average response time. Click any of these items to sort the table by that item. Click again to change the sort order.
- Total number of comments your teammates shared about the collection run. Click
(number of comments) to go to the run results and open the comments in the sidebar.
Hover over an item to show the following options:
View Report - Click to open the full results for the collection run. Learn more about debugging run results.
Share - Click to share the results with another team member. This provides a link you can give to other team members to view the details of this run. You can also click
Invite people to invite teammates to your workspace. If you’re in an internal workspace only you can access, you can click Invite people to invite teammates to your workspace and then share the results.
View scheduled runs
The Scheduled tab shows all the scheduled runs for the current collection. The following are displayed for each scheduled run:
- The upcoming run’s scheduled time
- The name of the scheduled run
- The environment associated with the scheduled run (if any)
Hover over an item to show the following controls:
- View - Click to open a page detailing the scheduled collection run’s latest results.
View more actions - Click to pause, resume, edit, or delete the schedule.
View performance runs
The Performance tab shows past performance runs for the collection. You can view metrics for each run, including the number of virtual users (VUs), duration, total number of requests, requests per second, average response time, and error rate.
Click a run to view a graph and full details for the performance run. Learn more about viewing performance metrics.
Automate collection runs
In addition to running collections manually, you can schedule collections to run automatically at specified times in the Postman cloud. You can also use collection runs with other Postman utilities to build automation into your API projects:
- Use the Postman CLI command-line interface to run collections and build them into your development pipeline, responding to test outcomes to support your API performance.
- You can also use Newman to run collections from the command line.
- Adding a monitor to your collection lets you schedule collection runs and stay informed of any issues.
- You can also set up a collection webhook to trigger a collection run at a specific time with your own custom payload.
Next steps
Build on the Collection Runner fundamentals you’ve learned with the following topics:
-
Use scripts to build workflows with conditional sequences for running the requests in your collections. To learn more, go to Customize request order in a collection run.
-
Run your collections on a schedule to automatically test the functionality of your APIs. To learn more, go to Automate collection runs on a schedule.
-
Use the Collection Runner to test the performance of your API with the same requests, collections, and environments you use for functional API tests. To learn more, go to Simulate user traffic to test your API performance.